
SIM Swap
The prevalence of SIM Swap is increasing globally.
This type of fraud occurs when an unauthorized individual gains access to an individual’s SIM card, enabling them to redirect all communication to their device. As a result, the victim’s phone loses the network connection, and all communication is transferred to the fraudster’s phone. Then, the fraudster can misuse an SMS One-Time-Password (OTP) sent to the fraudster’s mobile phone to authenticate and finalize Account Takeover (ATO). ThreatMark’s deep behavior profiling detects any unusual authentication activity and prevents ATO.
TALK TO A FRAUD FIGHTER
The impact of SIM swap scams.
-
68Mdollars were lost to Americans in 2021, due to SIM swapping attacks.
-
20%year over year increase in SIM swaps.
-
12Mdollar cost to consumers in 2021 due to SIM swaps, says FBI.
Prevent SIM Swap fraud by analyzing typical user behavior and spot anomalies instantly.
The fraudsters, frequently organized by well-structured criminal organizations, use advanced social engineering techniques, such as impersonation, to manipulate phone service providers, allowing them to port the victim’s phone number and maintain complete control over communication. With it, they can obtain the SMS OTP used as a second authentication factor to pursue a complete ATO.
To finalize ATO, the fraudster must follow up by enrolling their device. That is precisely where ThreatMark can intervene, identifying the signals of ATO by analyzing abnormalities in:
- Device fingerprint, location, login time, IP address and Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- Deep behavior profiling, supported by behavior biometrics (device handling, swiping & typing patterns, and more)
- Consequent payment anomalies
Such a holistic overview can effectively combat SIM Swap regardless of its unconventional nature.

Preventing SIM swap scams
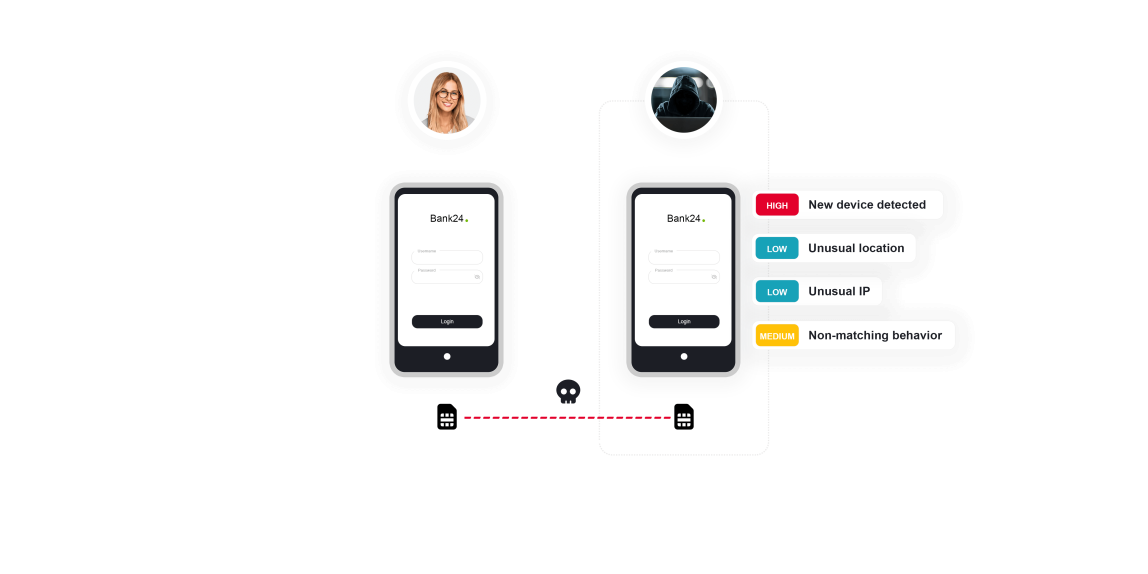
Detecting SIM swap attacks.
-
Remote Access Attacks
Legacy fraud prevention measures have limited effectiveness in detecting remote access attacks. When a session is controlled remotely by fraudsters, the bank's systems may identify the device as trusted based on its fingerprint, which may not show any signs of malware and appear to have the correct IP and geo-location.
-
Phishing Site Detection
Fraudsters use increasingly sophisticated methods to deceive users into revealing their login credentials. The fake pages they create are fully automated and very convincing. Moreover, they are using advanced evasion techniques to bypass traditional detection measures.
Want to learn more about ThreatMark?
Complete our form to discover more about ThreatMark’s comprehensive approach to fraud disruption.